- Do you need help? Here Us:
- +91 98857 04874
- mathesis@mathesis.co.in
INDUSTRIAL DRYERS MANUFACTURERS
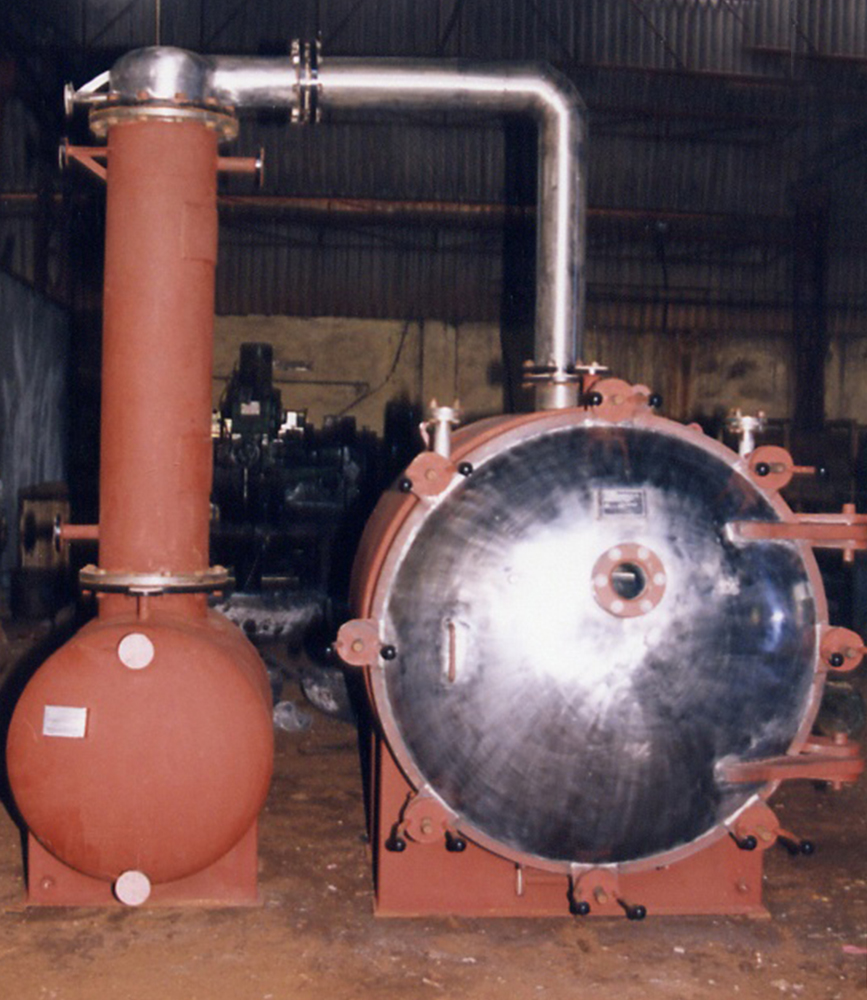
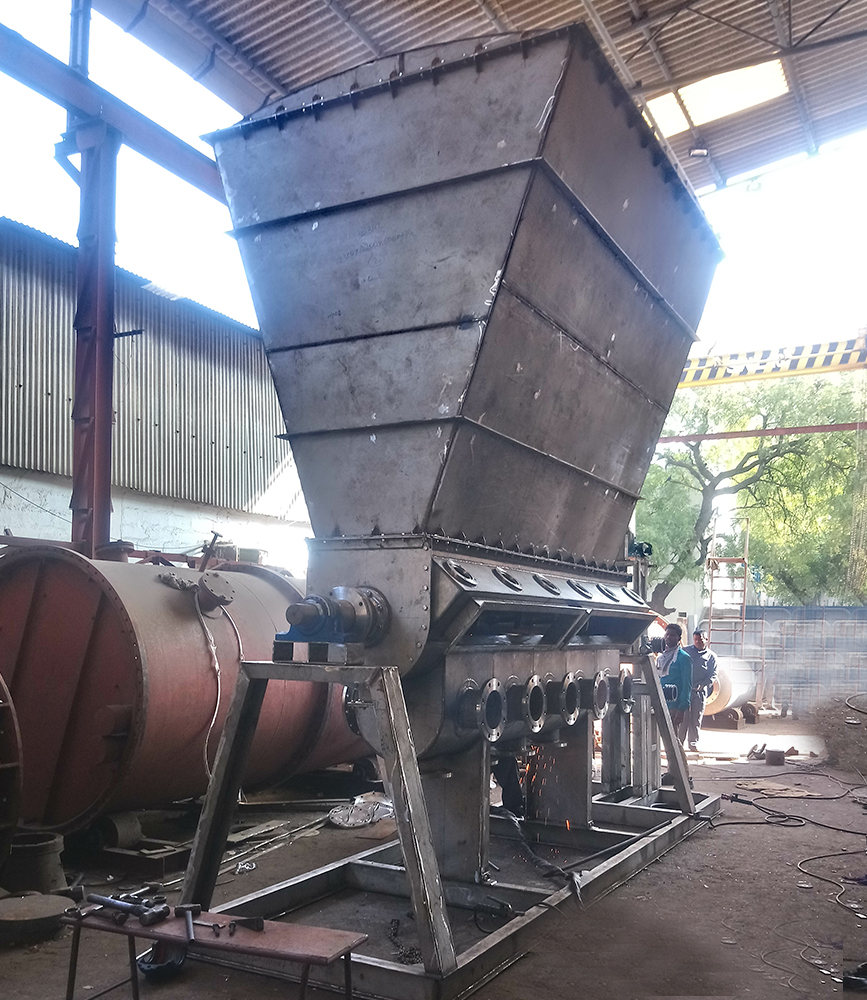
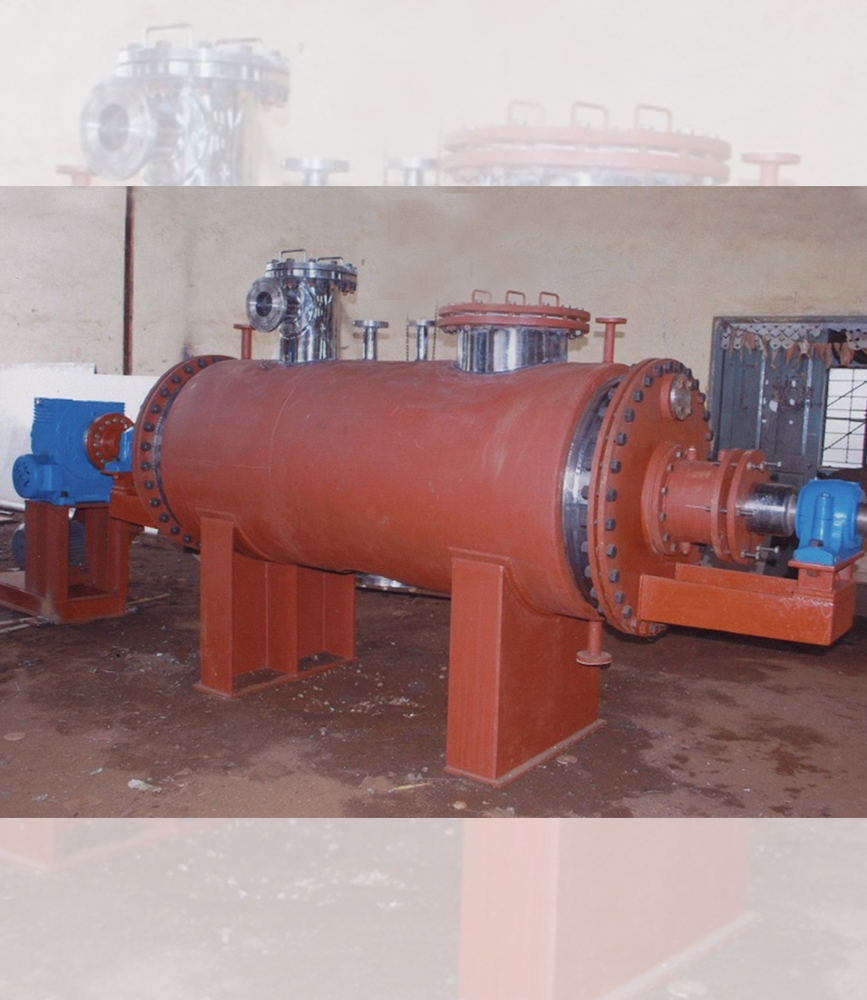
Mathesis are the leading Industrial Dryers Manufacturers. Drying is an operation in which moisture / Solvent is removed thermally from a liquid / solid mixture. Dryers vary in application and function.
Selection Of Drying Equipment
# Initial Selection of Dryer
- Best Suited to Handle the Wet Material and the Dry Product.
- Which fits into the Continuity of process as a whole.
- Which will produce a product of the desired Physical Properties.
Factors to consider in the preliminary selection of dryer are below
- Properties of the material being handled
- Drying Characteristics of the material
- Flow of material to and from the Dryer
- Product qualities
- Recovery Problems
- Facility available at site of proposed installation
# Initial Comparison of Dryers
- Evaluation of Size and Cost should be made to eliminate the uneconomical process
# Drying Tests
- Drying tests need to be conducted on the selected Dryers. These tests will determine the optimum operation conditions and product characteristics.
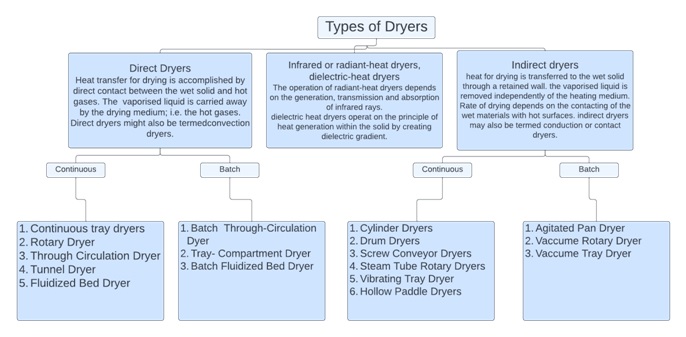
Classification of Dryers Based on Material Handled
| Material Type | Characteristics | Examples | Ideal Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquids | True & Colloidal Solutions, Emulsions | Inorganic Salt Solutions, Extracts, Blood, Waste Liquors, Rubber, Latex | Drum(Single or Twin), Indirect Continuous Dryer(Rotary Vacuum Dryer), Agitated Thin Film Dryer, Spray Drying |
| Slurries | Pumpable Suspension | Pigment Slurries, Soaps & Detergents, Calcium Carbonate, Bentonite, Clay Slip, Lead Concentrate | Screw Conveyor Dryer, Vacuum Shelf Dryer, Evaporator Crystallizer |
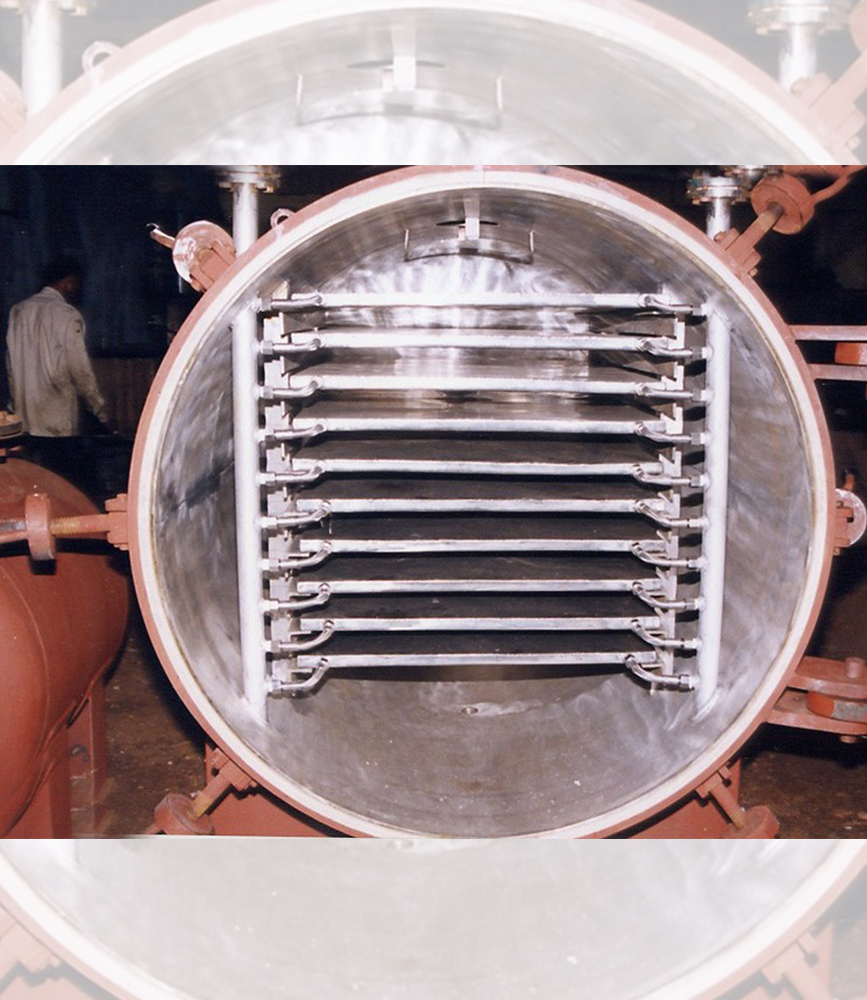
| Pastes & Sludges | - | Filter Sludges, Centrifuged Solids, Starch | Hollow Paddle Dryer |
| Free Flowing Powders | Small Partical Size, relatively free flowing in wet state, Dusty when Dry | Centrifuged Precipitates, Pigments, Clay, Cement | Fluidized Bed Dryer, Tray Dryer |
| Granular, Crystalline, Fibrous Solids | Larger Particle Size | Rayon Staples, Salt Crystals, Sand, Ore Potato Strips | Tray Drying, Tunnel Dryer, Rotary Dryer, Drum Dryer |
| Large Solids, forms or Shapes | - | - | Tray Drying, Tunnel Dryer, Rotary Dryer |
| Continuous Sheets | - | Paper, Fabric, Plastic Sheets | Rotary Dryer, Drum Dryer |
| Discontinuous Sheets | - | Veneer, Photograph Printing, Leather | Rotary Dryer |
Being leading Industrial Dryers Manufacturers, We at Mathesis Engineers Pvt Ltd., have conducted numerous Pilot Trials and Tried to understand the Nature of the Feedstock to be dried to the desired Moisture Levels or Residual Solvent Levels keeping in view the Process Economy.
Our Successful Pilot Trials which resulted in Equipment Solutions for our Customers are mentioned Below:
1) Thermal Desorption of Drilled Mud using Hollow Paddle Dryer
2) Agro Chemicals Drying-Spin Flash Dryer
3) Effluent Drying-Twin Drum Dryer
4) Hygroscopic Pharma Intermediates Drying-Contionous Fluidised Bed Dryer
5) Agrochemicals Drying-Vaccum Drum Dryer
6) Protein Concentration-Agitated Thin Film Evaporator
7) Agrochemicals Dryer-Continous Screen Conveyor Dryer
8) Biomass Drying-Hollow Paddle Dryer
9) Agrochemicals Effluent Dryer-Agitated Thin Film Dryer